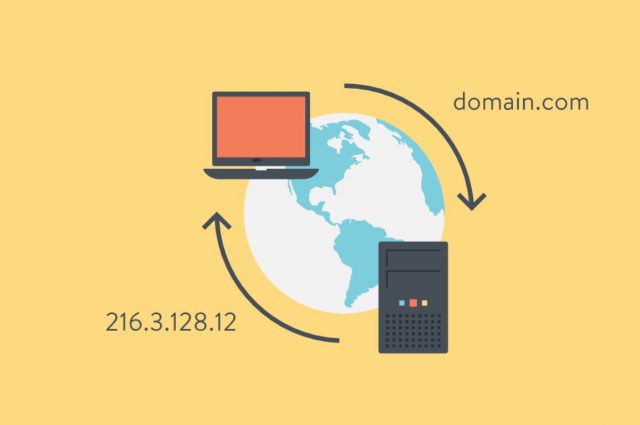
When you are using the internet, you think it’s just about clicking to connect, and that’s all. A layperson might be aware of a few additional terms like server, Cloudflare, etc. Still, behind the scene, there is a whole network of so many different things, technologies, and components that make the website and its related information available to you. among the many things, processes, and technologies, DNS is a prominent one.
The DNS or domain name system is something that ensures your internet is working exactly the way you want it to. However, with the constant evolution of technology, growing need for the internet, and growing use, there is a need to upgrade the system and add more features to it constantly. The features in the IT/Computer language are called records.
For efficient working of domains and hostnames, you can find several DNS record cheat sheets. These sheets provide you detailed understanding and help in managing everything related to your website. For high-quality cheat sheet services, visit https://constellix.com/news/dns-record-types-cheat-sheet (Records Types Cheat Sheet).

What are DND records?
The main purpose of a DNS server is to create DNS records. It provides essential information about the hostname and the domain, and especially the IP address. In simple words, a DNS system can’t work without its records. Although there are several types of common DNS records that are used, the technology keeps on evolving, and different types of DNS records are constantly coming into the light. Some of the most common types of DNS records are as follows:
- Address Mapping record or A
- IP Version 6 Address record or AAAAAA
- Canonical Name record or CNAME
- Mail exchanger record or MX
- Name Server records or NS
- Reverse-lookup Pointer records or PTR
- Certificate record or CERT
- Service Location or SRV
- Text Record or TXT
- Start of Authority or SOA
Here is a detailed description of each DNS record and its purpose.

1. Address Mapping
Also known as A Record is among the most common type of DNS. It is also known as the host record. Its main purpose is to store a hostname. Furthermore, it is also a corresponding IPv4 address.
2. IP Version 6 Address
IP Version 6 Address record is commonly known as the AAAA Record. It is quite useful for storing hostname along with IPv6 address.
3. Canonical Name
The most commonly known name for Canonical Name record is the CNAME Record. It is a commonly used DNS entry. It is also used to identify a hostname or a domain name and point it to another hostname. When you request a record that is CNAME, the resolution process takes place under a new hostname.

4. Mail exchanger (MX)
Mail exchanger record or MX Record is a type of DNS record that helps to move the emails as per the preference of the domain owner. It works on the outgoing emails and routes them to the specific email server.
5. Name Server (NS)
Name Server records or NS Record is a type of record that is used to specify a DNS zone. For instance, “abc.com is a domain name that is authorized to a specific AND or Authoritative Name Server. Thus, the NS record provides the complete address for that particular name server.
6. Reverse-lookup Pointer (PTR)
PTR Record or Reverse-lookup Pointer records are a type of record that allows the resolution center of DNS to receive the hostname or give the IP address to the relevant person. It is also known as the DNS look-up as it is associated with the DNS resolution center.

7. Certificate (CERT)
CERT or certificate record might not be too common, but it is quite useful. Its main purpose is to store certificates like PGP, SPKI, PKIX, etc. these certificates are encrypted and provide several uses to the websites.
8. Service Location (SRV)
Service Location or SRV Record is a type that resembles the Mail exchanger record a lot. Where the MX record is useful for emails, the SRV is ideal for the service location of other protocols of communication. It is not as popular or as widely used as the MX record but has its uses.
9. Text Record (TXT)
Among all types of DNS components, the text record or the TXT is the only one that is specifically for the machine to read. It is a type of data that is readable by the machine only. For example, DKIM, sender policy framework, DMARC, and opportunistic encryption are a few types of data that are only for the machines to read.
10. Start of Authority (SOA)
Start of Authority or SOA Record is quite a crucial type. Because it appears at the start of the zone file, you get information about the specific AND for the required DNS zone. Furthermore, it also provides details of contacts regarding the administration of a particular domain. Also, it offers information about the serial number of a particular domain and concerning information about the flow of DNS information at any particular zone.
Although DNS is most commonly used for the information and its flow, there is a lot more this system or technology can do. Here are a few to note among the many different things a DNS server or system can do.
DNS can also provide a fast connection between different data centers that are connected with each other globally. It can also work for identifying the information about the user. This information includes finding the physical location etc. it can also control the flow of traffic across the domains and the hostname. Lastly, it can also reduce the congestion or jamming of the flow of traffic.
DNS records are important for carrying out different processes at the back end for someone who doesn’t know the DNS system. No network, internet, or website can work without it, and that’s why it is crucial.